Heart disease or Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease (CVD), remains the leading cause of death worldwide. It accounts for millions of deaths each year and poses a significant burden on global healthcare systems. Despite advances in medical science, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures, the prevalence of heart disease continues to rise. Understanding the reasons behind its dominance among fatal illnesses can help individuals and communities take proactive steps toward prevention and management.
The Global Impact of Cardiovascular Disease
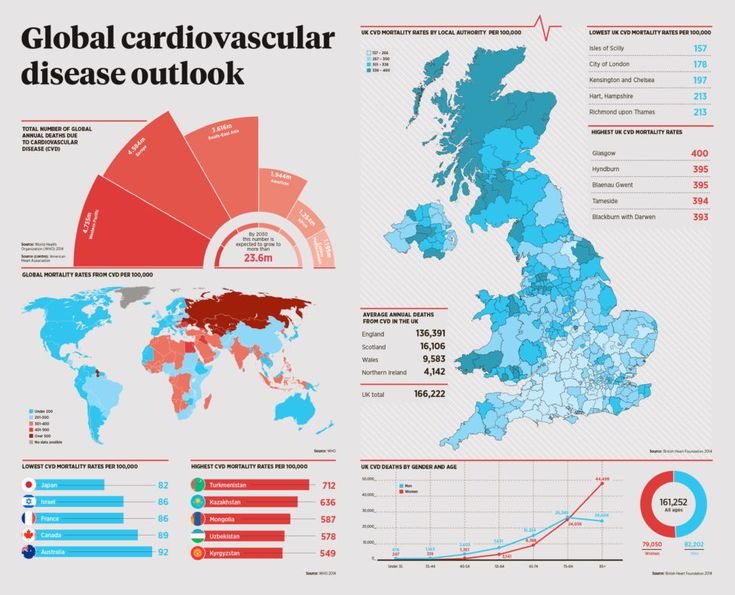
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), cardiovascular diseases are responsible for approximately 17.9 million deaths annually, representing around 31% of all global deaths. These diseases encompass various conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, stroke, and hypertension-related complications.
The burden of heart disease is not confined to developed nations; it affects both high-income and low-income countries. However, low- and middle-income nations face higher mortality rates due to limited access to healthcare, lack of awareness, and lifestyle factors contributing to heart disease risk.
Causes and Risk Factors of Heart Disease
Heart disease develops due to multiple factors, including genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and environmental influences. Some of the most common causes and risk factors include:
1. Unhealthy Diet
A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and refined sugars increases the risk of heart disease. Excessive consumption of processed foods, fast food, and sugary beverages leads to obesity, high cholesterol, and hypertension, which are significant contributors to cardiovascular diseases.
2. Lack of Physical Activity
Sedentary lifestyles are another major risk factor for heart disease. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces blood pressure, improves blood circulation, and enhances overall heart function. The modern era of technology and automation has significantly reduced physical movement, contributing to rising cases of heart disease.
3. Tobacco Use and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease. It damages blood vessels, reduces oxygen supply to the heart, and increases the risk of plaque buildup in arteries. Similarly, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to high blood pressure, obesity, and heart failure.
4. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
Hypertension, often called the silent killer, significantly increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes. It occurs when the force of blood against artery walls is too high, leading to strain on the heart and blood vessels.
5. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Individuals with diabetes are more prone to heart disease because high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. Metabolic syndrome, a combination of obesity, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, further elevates the risk.
6. Obesity
Obesity is a growing global epidemic that directly contributes to heart disease. Excess weight puts additional strain on the heart, leading to conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol, all of which increase cardiovascular risk.
7. Stress and Mental Health
Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Stress hormones can elevate blood pressure, lead to unhealthy eating habits, and increase inflammation in the body, all of which negatively affect cardiovascular health.
Why Is Heart Disease So Prevalent?
Despite growing awareness and medical advancements, heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Several factors contribute to its widespread prevalence:
1. Aging Population
As life expectancy increases, more people are living longer, which naturally increases the risk of age-related diseases, including heart disease. Aging leads to the gradual weakening of the heart and blood vessels, making individuals more susceptible to cardiovascular conditions.
2. Urbanization and Lifestyle Changes
Rapid urbanization has led to lifestyle changes that promote sedentary behavior, unhealthy eating habits, and increased stress levels. The convenience of processed foods, reduced physical activity, and increased work-related stress contribute to the rising incidence of heart disease.
3. Lack of Preventive Healthcare
Many individuals do not undergo regular health check-ups, leading to late detection of heart disease. Conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes often go unnoticed until they cause severe complications.
4. Inequality in Healthcare Access
In low and middle-income countries, access to quality healthcare is limited. Many people cannot afford preventive screenings, medications, or necessary medical procedures, increasing mortality rates from cardiovascular diseases.
Preventing Heart Disease
While heart disease remains the leading cause of death, many of its risk factors are preventable. Here are some key preventive measures:
1. Adopting a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can reduce the risk of heart disease. Avoiding processed foods, trans fats, and excessive sugar intake is essential for maintaining heart health.
2. Regular Exercise

Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can significantly improve cardiovascular health. Activities such as walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling help strengthen the heart and improve blood circulation.
3. Quitting Smoking and Limiting Alcohol
Eliminating tobacco use and reducing alcohol intake can lower the risk of heart disease and improve overall health.
4. Managing Stress
Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help maintain heart health. Engaging in hobbies, spending time with loved ones, and maintaining a work-life balance also contribute to stress reduction.
5. Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine medical check-ups, including blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol level checks, and diabetes screening, can help detect risk factors early and prevent complications.
6. Medication and Medical Interventions
For individuals with existing heart conditions or high-risk factors, medications such as statins, blood pressure-lowering drugs, and anticoagulants can help manage the disease and reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.

Do You Know
- Revolutionizing cardiology recent advancements in heart disease treatment. click here to know some interesting facts.
- What happens when cholesterol is high? How to manage it? Click here and know some interesting facts about it.
Conclusion
Heart disease continues to be the leading cause of death worldwide due to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. However, it is largely preventable through healthy lifestyle choices, early detection, and effective medical interventions. Raising awareness, promoting heart-healthy habits, and ensuring access to healthcare can significantly reduce the global burden of cardiovascular diseases. By making informed decisions and taking proactive steps, individuals can protect their hearts and live longer, healthier lives. If you want consultation with a cardiologist, get an immediate appointment with the best cardiologist in Dubai.